Quickstart Guide
Docker
First pull and run a NATS server:
docker run --rm -d --name nats_server -p4222:4222 nats --jetstreamthe SHAR server:
docker run --rm -d -eNATS_URL=nats://nats_server registry.gitlab.com/shar-workflow/shar/dev/server:latestand the SHAR BPMN editor:
docker run --rm -d -p 8080:80 registry.gitlab.com/shar-workflow/shar-ui/dev/bpmn-editor:latestthen download the shar-cli:
wget -o shar https://gitlab.com/shar-workflow/shar/-/package_files/265496511/download
mv download shar
chmod +x shar
sudo mv shar /usr/local/bin/now you can use the shar-cli to interact with the server.
First create an example service called helloworld.yaml:
shar util template-task helloworldThis will create a helloworld.yaml file in the current directory. The content of the file will look similar to this:
version: '1.0'
# Task type. Use "UserTask" for defining UI tasks.
kind: ServiceTask
metadata:
# optional: A category for grouping tasks.
category: communications
# The name of the task when called from the workflow.
type: helloworld
# A short description of the task.
short: Send an email.
# A full description of the task.
description: Send an email using the external email service.
# optional: A set of labels for the task for searching and filtering..
labels:
- email
# A manual version number for the task. This can be used to force
# the version hash of the task to change when updating the task definition.
version: 0.0.1
behaviour:
# Mock task. If true, the task will evaluate the expressions defined
# in the example fields in the output variables section instead of
# calling the Service Task code.
mock: false
defaultRetry:
# Number of retries before the service task is marked as failed.
number: 30
# Retry strategy:
# 0 = Linear. The task will be retried after the specified interval.
# 1 = Exponential. The task will be retried after the specified interval,
# multiplied by the number of previous retries.
strategy: 1
# Initial retry interval in milliseconds.
initMilli: 30000
# Multiplier for the retry interval.
intervalMilli: 10000
# Ceiling for the retry interval in milliseconds.
maxMilli: 120000
defaultExceeded:
# Action to take when the maximum retry interval is reached:
# 0 = Pause the workflow and await manual intervention.
# 1 = Throw a WorkflowError.
# 2 = Set a workflow variable to indicate the task has exceeded its
# retry limit.
# 3 = Fail the workflow.
action: 3
# Maximum estimated duration of the task in milliseconds.
estimatedMaxDuration: 2343255
parameters:
# optional: Parameter groups for organizing parameters into logical blocks.
parameterGroup:
# The name to be displayed in the UI.
- name: group1
# A short description of the parameter group.
short: Email parameters
# A full description of the parameter group.
description: Email parameters
# optional: Variables which will be passed to the Service Task.
input:
# The name of the parameter as it will appear in the workflow.
- name: Address
# A short description of the parameter.
short: Address field.
# A full description of the parameter.
description: An email address to send the email to.
# The type of the parameter:
# string: A string value.
# int: An integer value.
# bool: A boolean value.
# float: A floating point value.
type: string
# The group specified above that the parameter belongs to.
group: group1
#
mandatory: true
# An example value for the parameter.
# This is used as input during mocking if no parameter value is specified.
example: "= 'joe@example.com' "
# optional: Variables which will be returned from the Service Task.
output:
# These parameters have the same structure as the input parameters.
# The example parameter will be used as the output when mocking a task.
- name: Success
short: A success flag.
description: True if the email was sent successfully.
type: string
group: group1
mandatory: true
# An example value for the output parameter.
# This is used as output during mocking. It has access to the input parameters.
example: "= true "
events: {}Register the helloworld service with the server:
shar servicetask add helloworld.yamlThis tells the server that a new service is available that can respond to service task requests.
Now create an implementation for the helloworld service using the shar CLI:
shar util create-service --output helloworld helloworld.yaml
cd helloworld
go mod tidyThe CLI created a helloworld directory contining the service implementation. Most of it is autogenerated code. The implement folder contains the editable code for your service.
Edit implement\helloworld.go in your favourite editor.
package implement
import (
"context"
"gitlab.com/shar-workflow/shar/client/task"
)
// Helloworld - Send an email using the external email service.
func Helloworld(ctx context.Context, client task.JobClient, address string) (success string, err error) {
//TODO: Implement the functionality for helloworld here.
return
}add the following to the import section at the top:
"fmt"And the following lines under the TODO comment:
fmt.Printf("Hello world from %s\n", address)
success = "true"You have created your first workflow service.
Before starting it, convert the helloworld.yaml file to a ‘contact-sheet’ so we can use it in a workflow.
shar util contact-sheet --output sample.bpmn spec/helloworld.yamlThis produces a BPMN 2.0 XML file called sample.bpmn containing our service task as a BPMN shape. We can now use this file to create a business process in the SHAR BPMN Editor later.
Now, build and run the service listener:
go build -o helloworld cmd/helloworld/main.go
./helloworldLeave this running so it can service requests from our business process.
From your browser open the SHAR BPMN Editor. If you are running it locally use: http://127.0.0.1:8080 if not you can run ours from: https://editor.go-workflow.com
Open the sample.bpmn file.
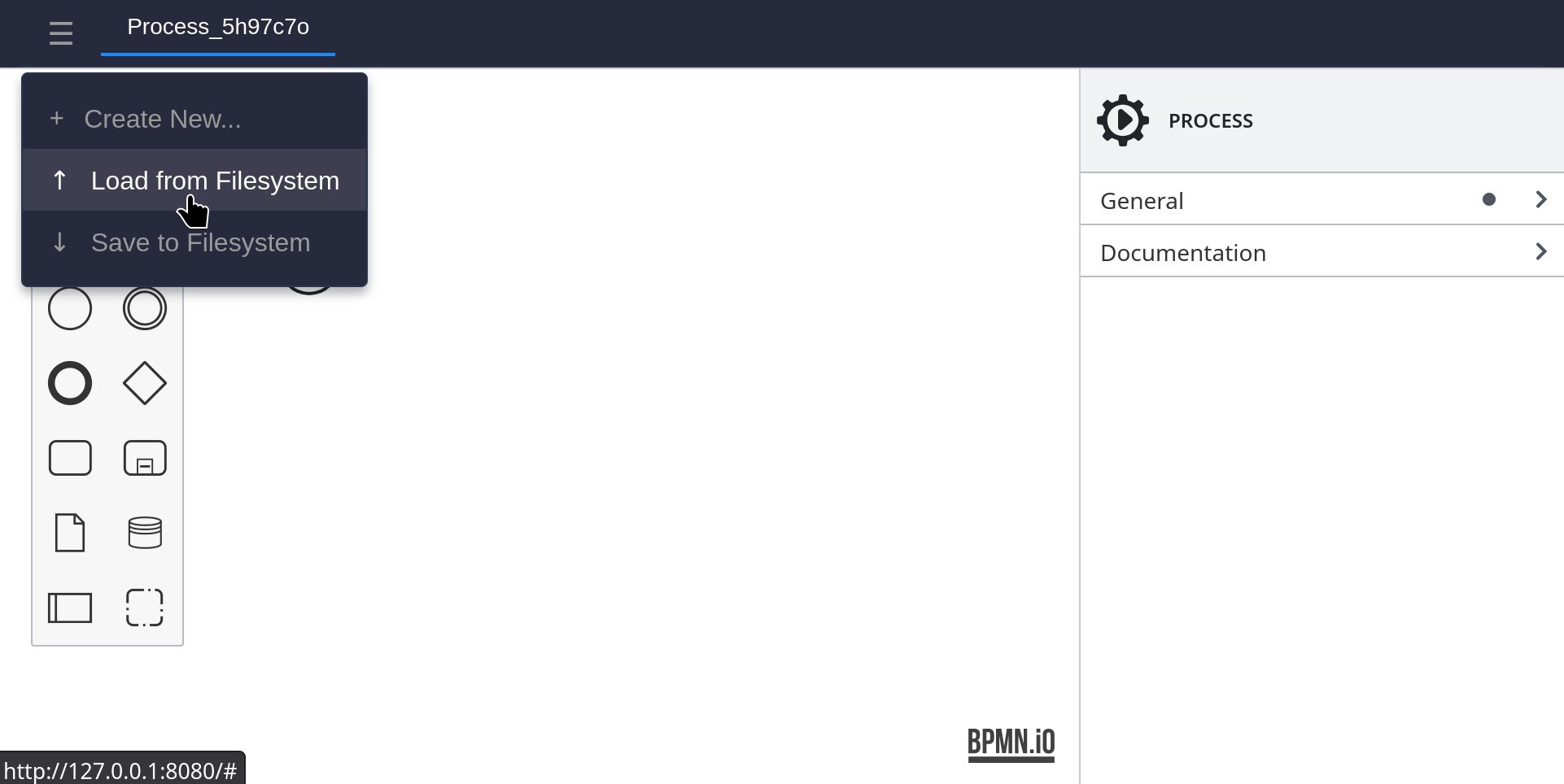
In the properties panel on the right, change the ID of the process, from ContactSheet to HelloWorkflow.
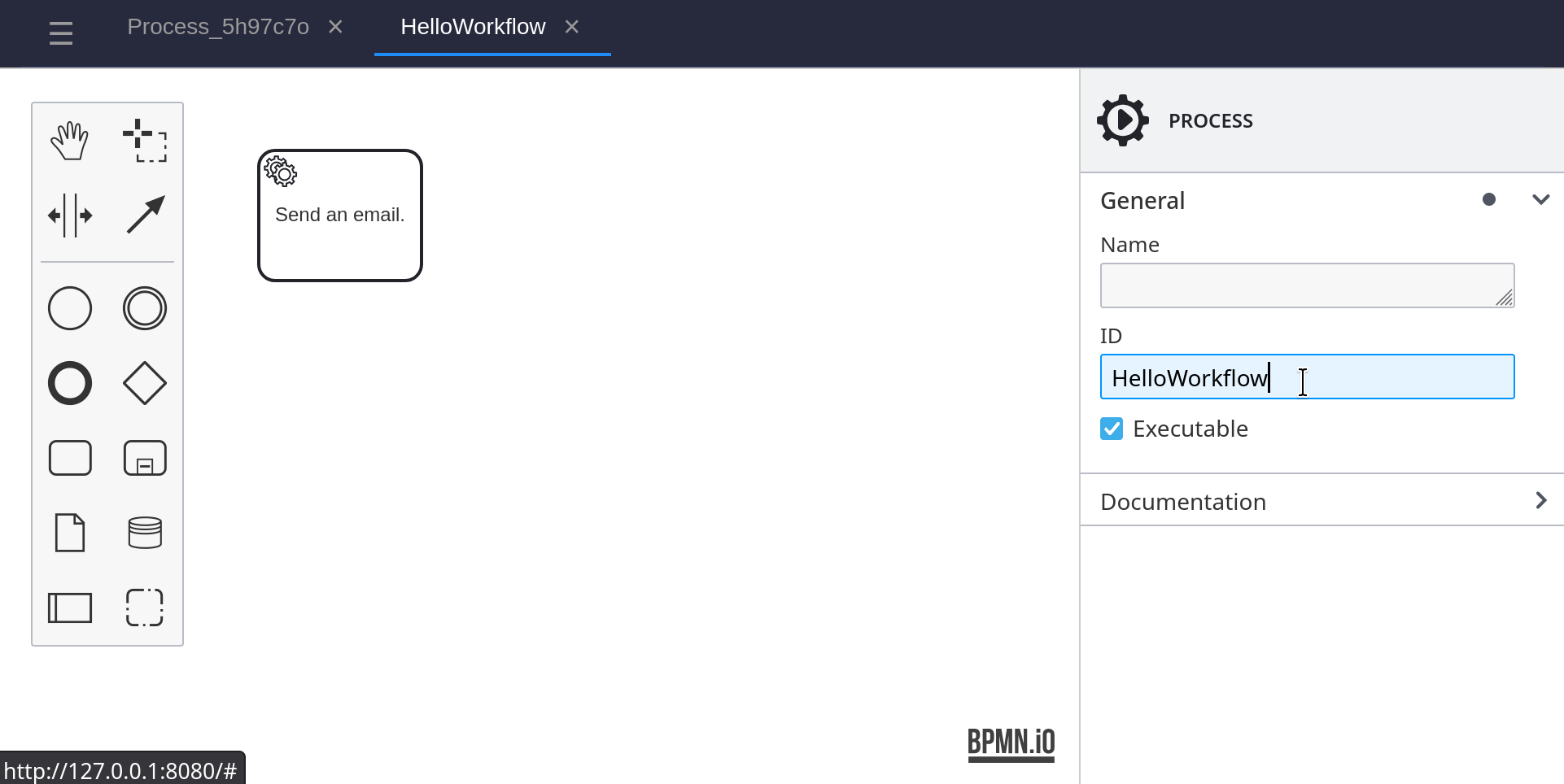
Add a Start Event to the BPMN diagram, and connect it to the service task. Create an Output Mapping and set the Process Variable Name to Address. Set the Variable Assignment Value to Address.
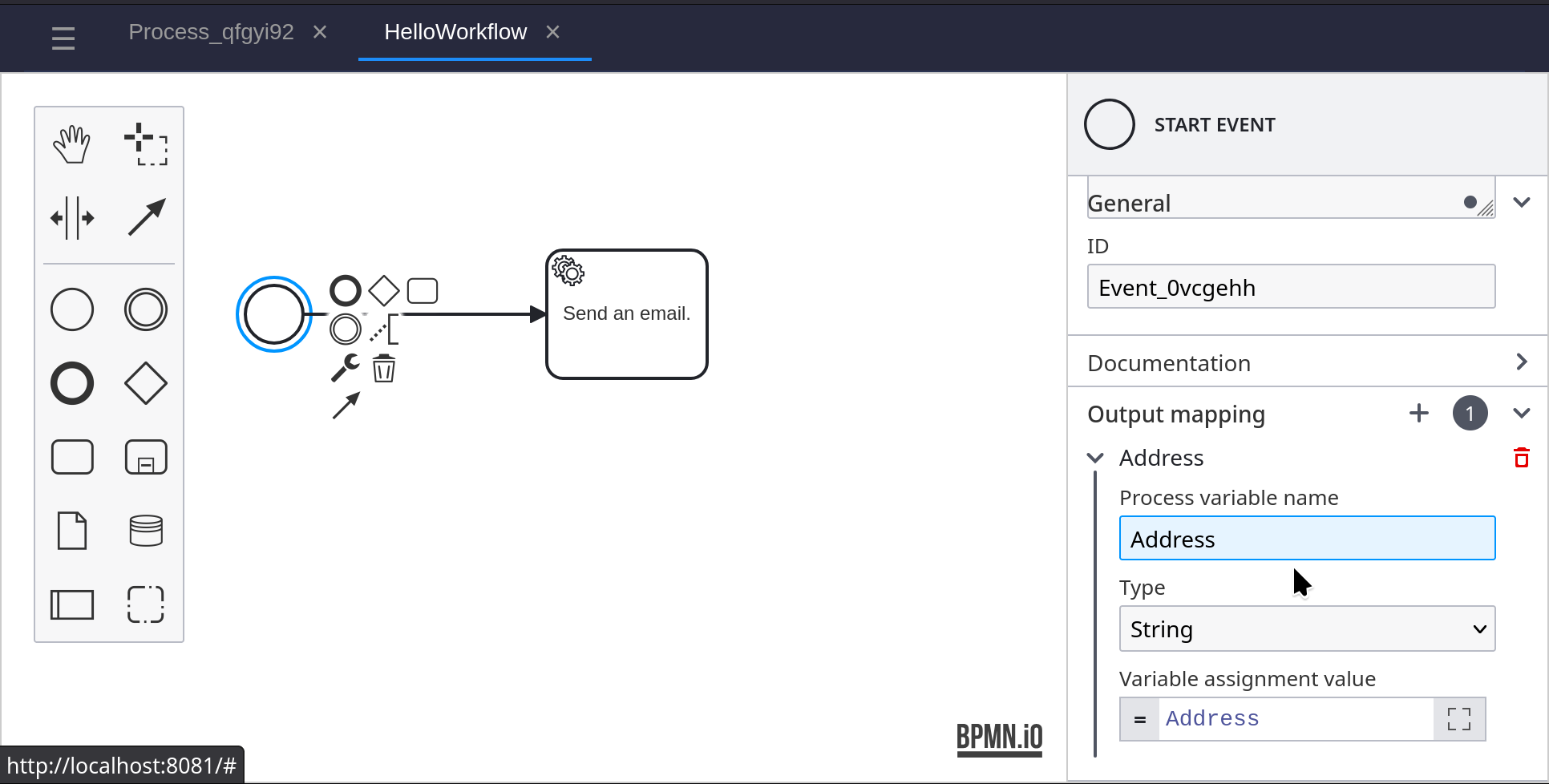
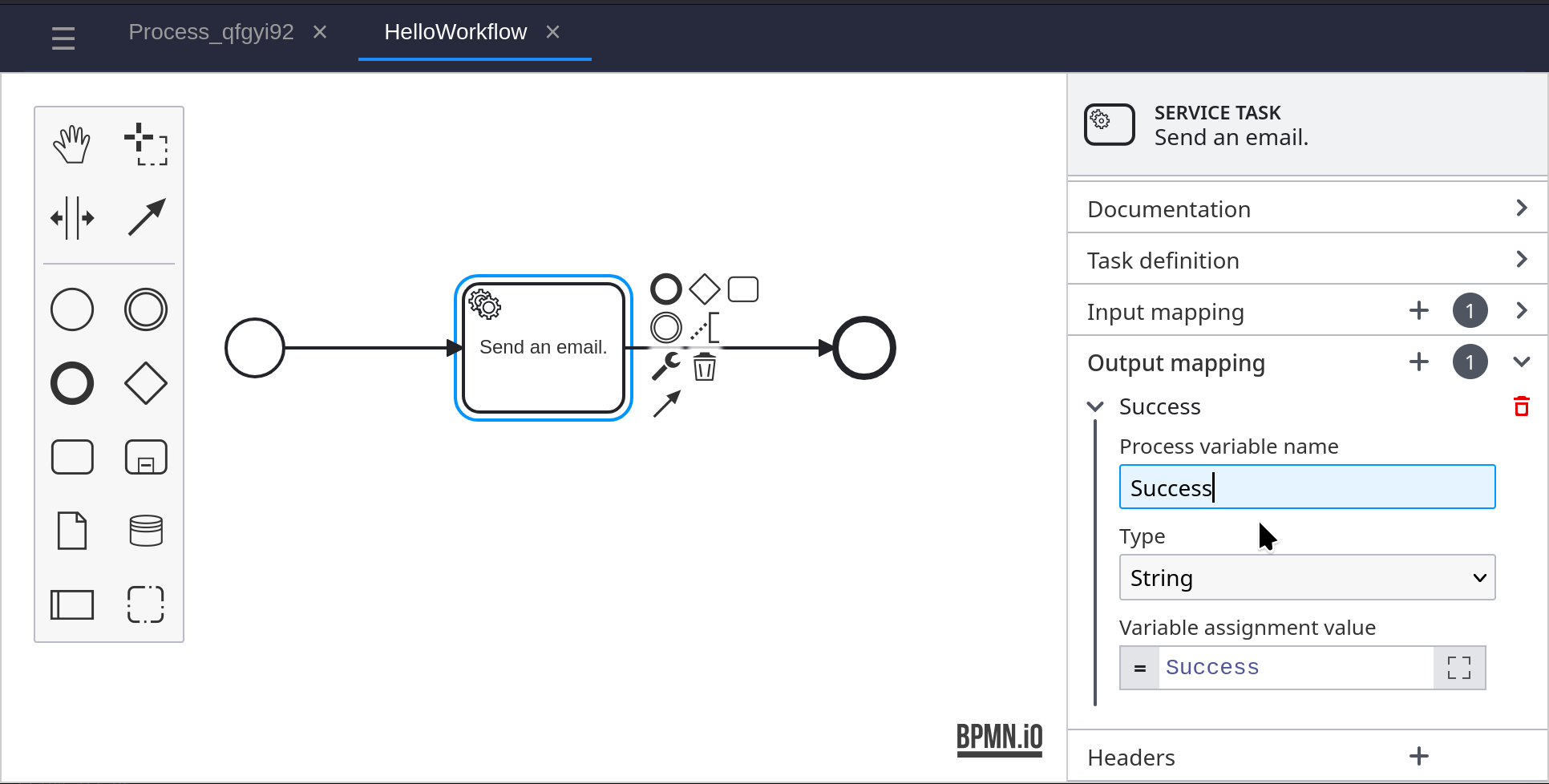
Add an End Event to the BPMN diagram, and connect it to the service task. Create an Output Mapping and set the Process Variable Name to Success. Set the Variable Assignment Value to Success.
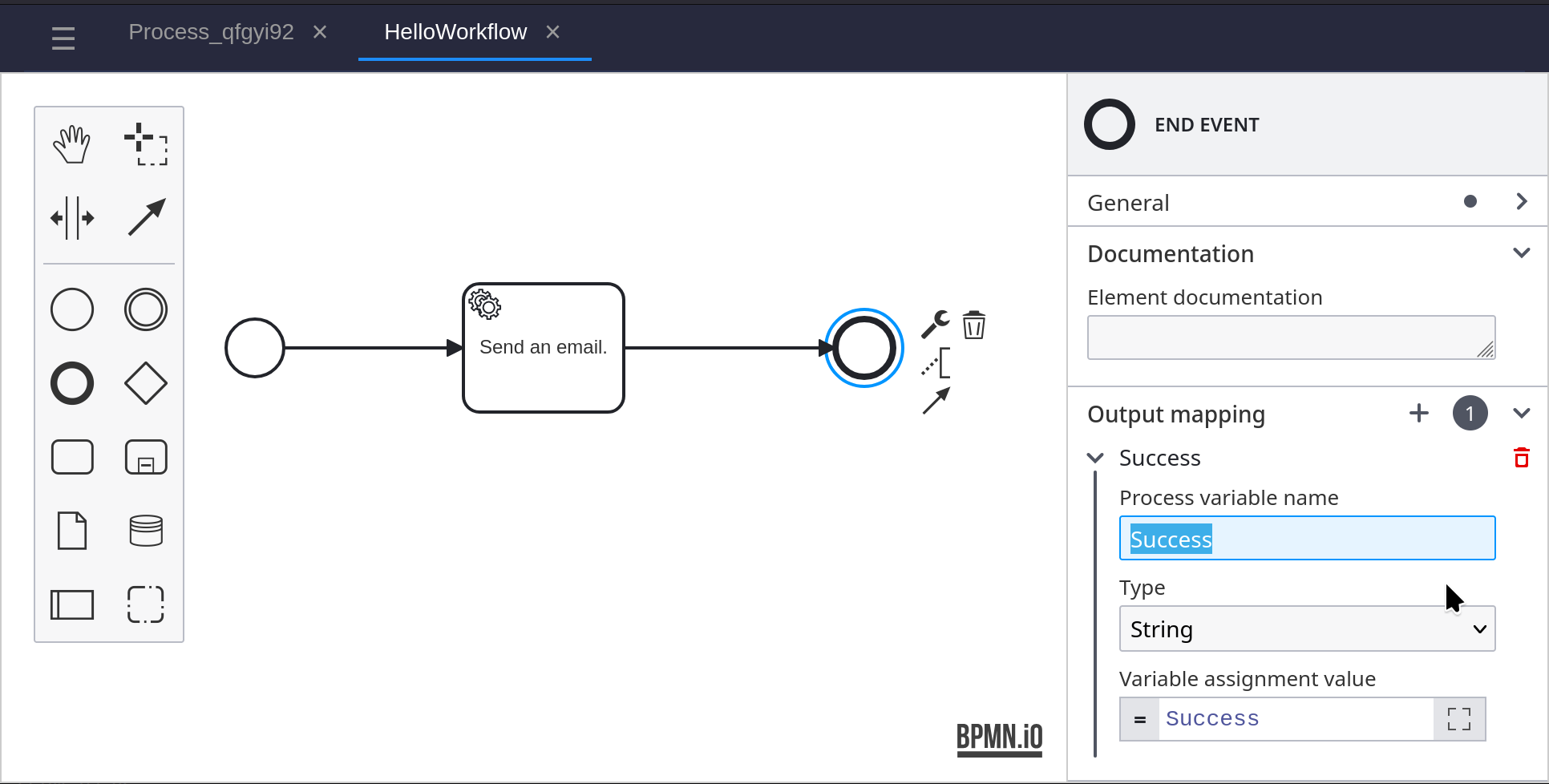
Click on the Service Task, and in the properties panel on the right. Under Input Mapping, set the Variable Assignment Value to ‘Address’.
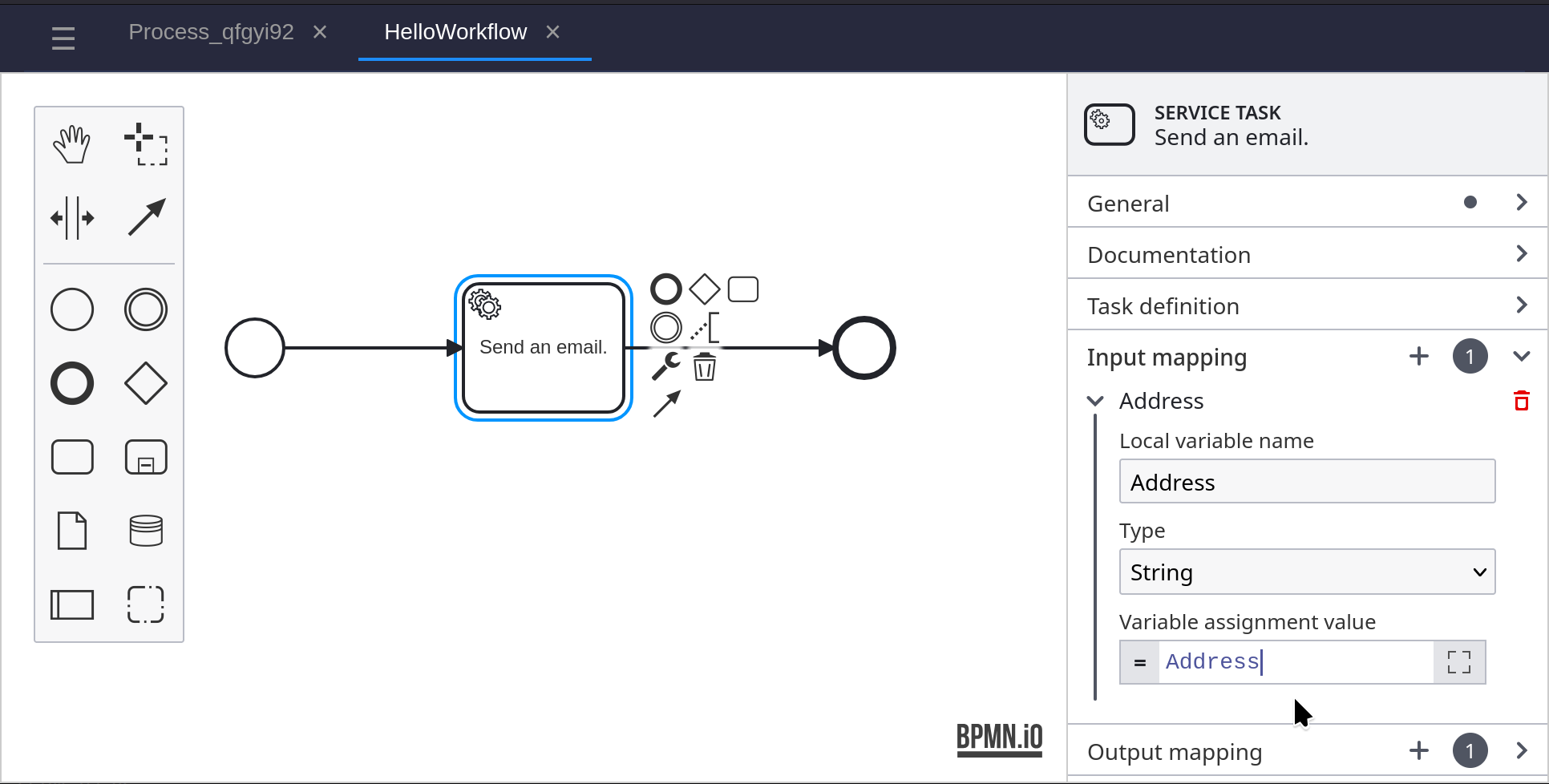
Under Output Mapping, set the Process Variable Name to ‘Success’
Save the BPMN diagram, and exit the modeler.
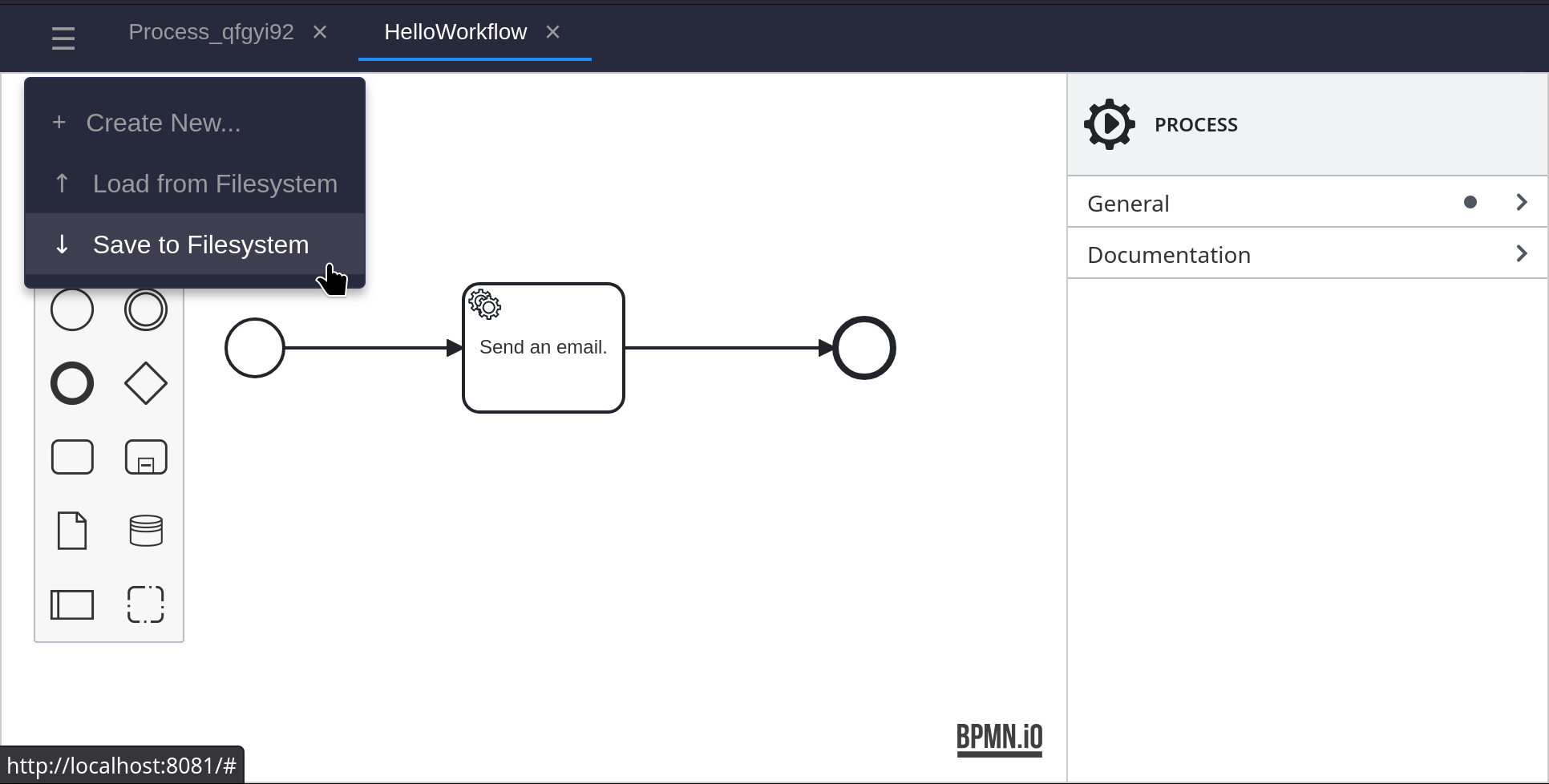
Copy the resulting sample.bpmn file to the helloworld directory.
Now load the BPMN into the server ready for execution:
shar bpmn load FirstBPMN sample.bpmnWe can now execute the process and watch the service task run. Note that we pass in the ‘Address’ workflow variable that our start event is expecting:
shar process start HelloWorkflow --vars="Address:string(sample@sample.com)"